Are you looking for a reliable way to fasten materials in your construction or industrial projects? Understanding the different types of thread bar and threaded rod is crucial for ensuring a strong and secure connection. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the various type of threaded rods available, their unique features, and their applications, helping you choose the right fastener for the job. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of thread.
What Exactly is a Thread Bar or Threaded Rod?
A thread bar, also known as a threaded rod or stud, is essentially a straight metal rod that features a continuous helical groove, known as a thread, running along its entire length. This threading makes it ideal for engaging with nuts and washers to fasten materials together. Unlike a bolt or screw, which typically has an unthreaded shank, a threaded rod is fully threaded from one end to the other. This design allows for maximum engagement and adjustability, making it a versatile fastener in various applications.
Threaded rods are available in a wide range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminium, each offering different levels of strength and durability, as well as corrosion resistance. The specific type of threaded bar you choose will depend on the environment and the load it needs to bear. These metal rod options are fundamental components in many construction and manufacturing processes.
What are the Different Types of Threaded Rod?
Understanding the different thread bar types is essential for selecting the correct fastener for your project. One common distinction is between fully threaded rods, where the thread runs along its entire length, and partially threaded rods, although the latter is less common when referring to threaded rod specifically. Material is another key differentiator. Steel threaded rod is commonly used for general applications requiring good strength. For environments where corrosion is a concern, stainless steel threaded rod provides superior resistance.
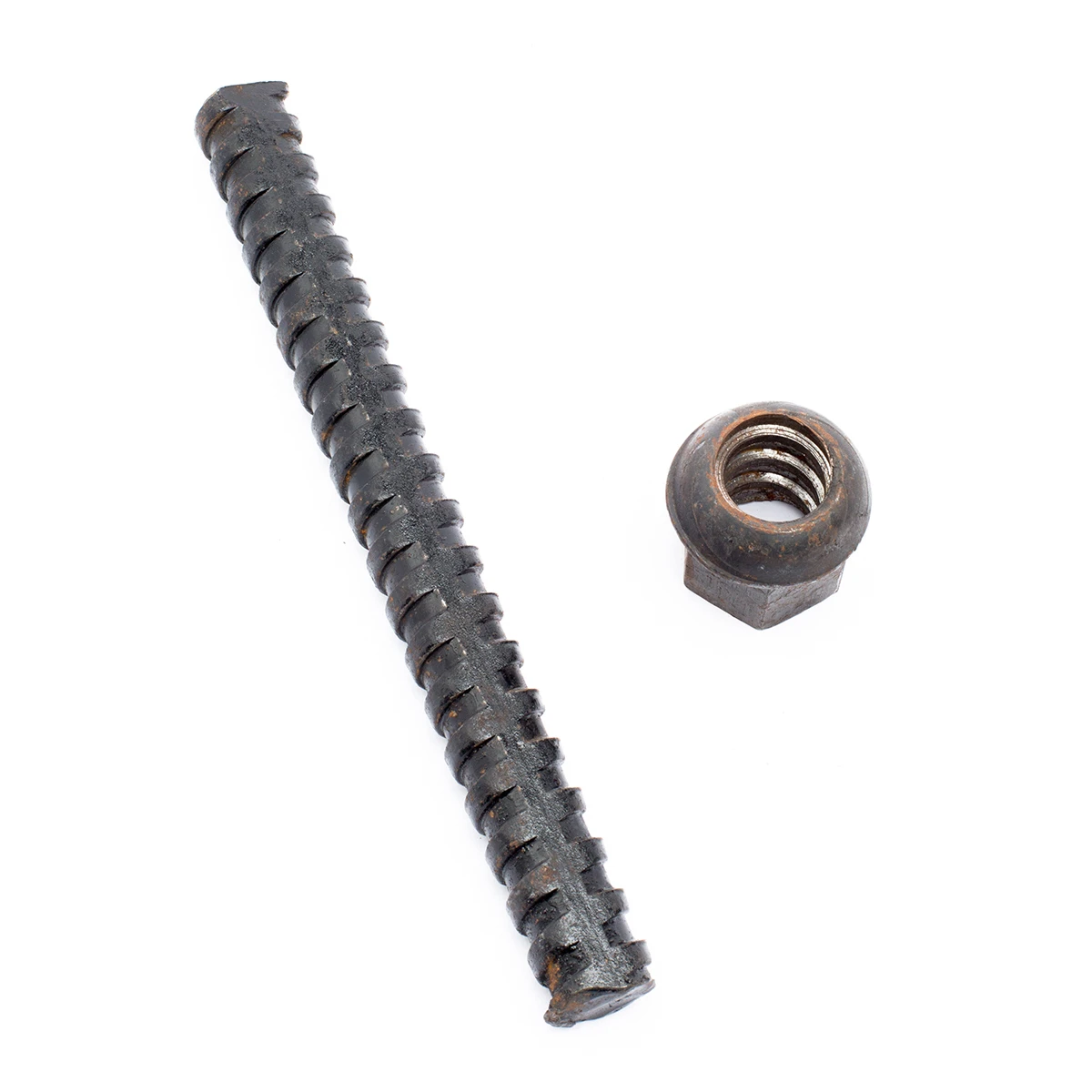

Alt: Various types of threaded rods
Beyond materials, the threading itself can vary. The thread pitch, which is the distance between thread crests, and the thread form (e.g., metric, imperial) are crucial considerations. You might also encounter specialized types like hollow threaded rods, which can be used for running wires or fluids through the center. The types of threaded rod are diverse to meet the demands of various engineering and construction needs.
How Do You Use Thread Bar Effectively?
To use thread bar effectively, you need to consider its intended purpose and the materials you are joining. The threaded rod is inserted through aligned holes in the materials, and then nuts and washers are applied to each end. Tightening the nuts creates a clamping force, securely fastening the materials together. The fully threaded nature of the bar allows for precise adjustments and clamping force distribution along the entire length of the rod.
Threaded bars are used in scenarios where adjustability is key. For example, in suspending ductwork or piping, the length of the rod can be adjusted to the exact required height. They also be used to create tensioning devices or as components in more complex assemblies. The versatility of the thread bar makes it an indispensable fastener in many industries.
What are the Typical Uses for Threaded Rod?
The uses for threaded rods are incredibly diverse, spanning numerous industries. In the construction industry, they are used to fasten and stabilize structures, suspend pipes and ducts, and create anchoring systems. Think of them being used to secure framework, scaffolding, and even signage. Their strength makes them ideal for heavy-duty construction applications.
Beyond construction, threaded rods find application in manufacturing, where they are used to create jigs, fixtures, and clamping mechanisms. They are also used in plumbing for securing pipes and in various DIY projects where a strong and adjustable fastener is needed. Essentially, anywhere you need to join materials securely with the option for adjustment, a threaded rod is a potential solution.
Guide to Threaded Rod Sizes: How Do You Choose?
Choosing the correct size guide for your threaded rod involves several considerations. The diameter of the rod is a primary factor, as it dictates the strength and durability of the fastener. Larger diameters offer higher load capacity. The thread pitch, measured as threads per inch or millimeters, also plays a crucial role. A coarser thread pitch will fasten more quickly, while a finer thread pitch offers more precise adjustments and greater holding power.
You also need to consider the length of the rod required for your specific application. Threaded bars are often available in standard lengths, but one of their advantages is that the bar can be cut to size using tools like a hacksaw or a rod cutter. Understanding the thread size, diameter, and length requirements ensures you select the appropriate threaded rod for a safe and effective connection.
Threaded Rod vs. Threaded Stud: What's the Difference?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there's a subtle distinction between a threaded rod and a threaded stud. A threaded rod is generally considered a longer metal rod that is fully threaded along its entire length. A threaded stud, on the other hand, may be shorter and can sometimes have unthreaded sections at either end. Think of a double-end threaded stud that is plain in the center with threading along both ends.

Alt: Close up of a nut engaging with a thread
However, in many practical applications, the terms stud and threaded rod are used to describe the same product: a straight metal component with threading running along its entire length. The key similarity is their fully threaded nature, which allows for maximum engagement with nuts and washers.
What are Threaded Rod Connectors and How are They Used?
Threaded rod connectors, also known as coupling nuts or rod couplings, are specialized fasteners used to join two threaded rod ends together. These connectors are essentially internally threaded sleeves that screw onto the threads of both rods, creating a continuous threaded section. They are particularly useful when you need a length of the rod that exceeds the standard threaded rod lengths available or when making repairs or modifications to existing threaded assemblies.
Threaded rod connectors are typically used in suspension systems, where long runs of threaded rod are needed for supporting pipes, ducts, or cable trays. They provide a strong and secure connection, ensuring the integrity of the suspended system. The use of these connectors eliminates the need for welding or other more complex joining methods, simplifying installation and adjustments.
Exploring Threaded Rod Hangers: Applications and Benefits
Rod hangers are specialized fasteners designed for suspending items from overhead structures using threaded rods. These hangers come in various forms, including beam clamps, swivel rings, and eye nuts, each designed for specific mounting scenarios and load capacity requirements. They work in conjunction with threaded rods to create adjustable and secure suspension systems.
Rod hangers are extensively used in the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) trades for suspending pipes, ducts, cable trays, and lighting fixtures. The combination of a rod hanger and a threaded rod allows for precise vertical adjustments, making installation easier and more efficient. The use of threaded rod hangers ensures a safe and reliable overhead support system in a wide range of construction applications.
Why is Cutting Threaded Rod to Size a Common Practice?
Cutting threaded rod to size is a commonly performed task due to the versatility it offers. While threaded rods are available in standard lengths, projects often require specific lengths that don't perfectly match these standards. The ability to cut to size ensures that the threaded rod fits the exact requirements of the application, minimizing waste and ensuring a proper fit.
Tools like hacksaws, bolt cutters, and specialized rod cutters can be used to achieve clean and accurate cuts. This practice is particularly important in applications where space is limited or where precise adjustments are needed. The ability to customize the length of the rod as required makes threaded rod a highly adaptable fastener.
Key Takeaways:
- A thread bar or threaded rod is fully threaded for maximum engagement.
- Different thread bar types exist based on material, thread pitch, and form.
- Threaded rods are versatile for fastening and suspension.
- Uses for threaded rods span construction, manufacturing, and plumbing.
- Choosing the correct size guide is crucial for load capacity and fit.
- Threaded studs are similar but may have unthreaded sections.
- Threaded rod connectors join threaded rod ends for longer runs.
- Rod hangers facilitate secure overhead suspension.
- Cutting threaded rod to size allows for customization.
- Threaded rods rely on threaded rods for strong and adjustable connections.
Post time: 12 月-26-2024