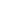
A bow spring centralizer is a crucial tool used in the oil and gas industry to aid in the effective and accurate placement of casing within a wellbore. Centralizers ensure that the casing remains in the center of the wellbore during cementing operations, allowing for a more uniform distribution of cement between the casing and the borehole. This process is essential for creating a proper seal to prevent gas, oil, or water from flowing between different layers of the well.
Bow spring centralizers are named for their flexible "bow-shaped" metal blades, which provide their unique functionality. Their primary role is to keep the casing centralized and prevent it from resting against the sides of the borehole. This article will explore how bow spring centralizers function, their importance in wellbore operations, and the challenges they address.
The Design of a Bow Spring Centralizer
At the heart of a bow spring centralizer is its distinct bow-shaped blades made from resilient steel or other materials. These blades are designed to bend and compress when inserted into the borehole, yet they exert outward force to push against the borehole walls, ensuring that the casing stays centered. The flexible nature of these blades allows the centralizer to accommodate changes in borehole diameter and imperfections in the wellbore.
The centralizer consists of:
- Bows or blades: These are the spring-like components that give the tool its name. They expand when under pressure, helping maintain a central position.
- Collars or end rings: These are rigid, circular components that secure the bows to the casing. The collars hold the centralizer in place and help transmit the force generated by the bows.
The flexibility of the bow spring design enables these centralizers to perform efficiently even in irregular boreholes, where the diameter might vary due to drilling imperfections. This is an advantage over more rigid centralizer types, such as solid-body centralizers, which may not be as effective in non-uniform boreholes.
Key Functions of a Bow Spring Centralizer
The bow spring centralizer serves multiple purposes in the drilling and cementing process:
- Centralizing the Casing: The primary function of a bow spring centralizer is to ensure the casing remains in the center of the wellbore. Proper casing centralization is critical to the successful completion of the well. If the casing is not centered, cement may not surround it, leading to poor isolation between the wellbore and the casing, which could cause leaks, contamination, or even well failure.
- Ensuring Proper Cementing: Effective cementing is essential for isolating different geological zones, which helps to prevent fluid migration between layers. By keeping the casing centered, the bow spring centralizer ensures an even layer of cement can be applied around the casing. Without proper centralization, cementing jobs can result in weak spots, leading to long-term integrity issues.
- Navigating Irregular Boreholes: The flexible bow design allows the centralizer to expand and contract as needed, adjusting to borehole irregularities. This flexibility is key in deviated, horizontal, or highly irregular boreholes where other types of centralizers may struggle. As the bows expand and press against the borehole walls, they create enough tension to keep the casing from contacting the sides.
- Reducing Drag: Bow spring centralizers are also beneficial in reducing the drag force when running casing down the wellbore. The spring action allows the centralizer to compress when encountering tight sections of the borehole, reducing resistance and allowing the casing to be inserted more smoothly.
Importance in the Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, ensuring the integrity of wells is of paramount importance. Any failure in the cementing process can lead to environmental damage, safety risks, and costly repairs. The bow spring centralizer plays a pivotal role in enhancing well integrity by optimizing the cementing process and improving the longevity of the well. Additionally, it helps to prevent communication between geological formations, which could lead to cross-flow of oil, gas, or water from different layers, potentially compromising the well's productivity.
Limitations and Challenges
While bow spring centralizers offer numerous advantages, they are not without limitations. One of the main challenges is that their flexible design can sometimes lead to reduced restoring force in highly deviated wells. In such scenarios, operators may need to use more centralizers or consider hybrid designs that combine the flexibility of bow springs with the strength of rigid centralizers.
Furthermore, the performance of bow spring centralizers can be affected by wear and tear, particularly in abrasive formations or highly deviated wells where friction is higher.
Conclusion
The bow spring centralizer is an indispensable tool in the oil and gas industry, playing a critical role in the cementing process and well integrity. Keeping the casing centered in the wellbore, ensures the proper application of cement, helping to prevent fluid migration and improve the well's longevity. Despite some limitations, its flexibility and adaptability to irregular boreholes make it a valuable choice in many good configurations.
Post time: 9 月-21-2024